You may have seen the City of Fullerton via their attorney Kim Barlow throwing around words like “thieves” and “hackers” in regards to the current litigation they initiated against us here at FFFF. You may have also seen the Fullerton Observer Pravda parroting their nonsense with their own “expert”.
In response we’ve decided to publish the bulk our tech expert’s declaration as submitted to the court for easy reading right here on the blog (CV, footnotes, et in link). We hope this helps clear up a lot of the BS being bandied around to baffle the masses by City Hall and their water carriers.
Please allow us to present the stellar work by John Bambenek.

Enjoy:
I. INTRODUCTION
I, JOHN BAMBENEK, hereby declare as follows:
1. The facts stated in this Declaration are true and correct of my own personal knowledge, except for those matters expressly stated on information and belief, which matters I believe to be true. If called as a witness, I could and would competently testify thereto.
2. I am filing this declaration in support of the Defendants Friends for Fullerton’s Future, Joshua Ferguson, and David Curlee’s Opposition to OSC re Preliminary Injunction sought by the City of Fullerton (“City”).
3. I have reviewed the following pleadings and documents filed in this case:
- Complaint for (1) Violation of Comprehensive Computer Data Access and Fraud Act (Cal. Pen. Code § 502 et seq.); (2) Violation of the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (18 U.S.C. et seq.); (3) Violation of Cal. Gov’t Code § 6204 et seq; Conversion; Trespass to Chattels; and (6) Conspiracy (filed by the City on October 24, 2019);
- Ex Parte Application for Temporary Restraining Order and Order to Show Cause as to why a Preliminary Injunction should not be issued; Memorandum of Points and Authorities (filed by the City on October 24, 2019);
- Declaration of Matthew Strebe and attached exhibits (filed by the City on October 24, 2019);
- Declaration of Mea Klein and attached exhibits (filed by the City on October 24, 2019);
- Declaration of Steve Lee (filed by the City on October 24, 2019);
- Declaration of Bruce Lindsay (filed by the City on October 24, 2019);
- Opposition to Plaintiff’s Ex Parte Application for an Unconstitutional Prior Restraint (filed by Defendants on October 25, 2019);
- Transcript of the October 25, 2019 Hearing on Plaintiff’s Ex Parte Application;
- Supplemental Memorandum of Points and Authorities in Support of Plaintiff’s
- Motion for Preliminary Injunction (filed by Defendants on November 1, 2019);
- Supplemental Declaration of Matthew Strebe (filed by Defendants on November 1, 2019);
- Supplemental Declaration of Mea Klein (filed by Defendants on November 1, 2019);
- Declaration of Christopher Tennyson (filed by Defendants on November 1, 2019);
- Declaration of Mike Rice (filed by Defendants on November 1, 2019);
- Declaration of Marni Rice (filed by Defendants on November 1, 2019); and
- Declaration of Ivy Tsai (filed by Defendants on November 1, 2019);
4. Based on my expertise and claims made in the declarations filed by the City (as set out in paragraph 3, above), I have reached the following conclusions:
- The City’s declarations do NOT substantiate any evidence of unauthorized access or “hacking” as those terms are typically defined;
- The use of a VPN or Tor is common among a wide variety of users, including journalists;
- The attribution of VPN traffic, Tor traffic, and other “foreign IP addresses” to Mr. Ferguson and Mr. Curlee is, at best, deeply flawed.
5. For purposes of this declaration and to aid the Court in its understanding of the issues presented in this case, I have created a Dropbox folder to simulate the underlying circumstances that gave rise to this case. I do not have any access to the documents that are at issue in this case, and do not have the ability to reconstruct the exact configuration or access the Dropbox account at issue since it has since been modified and is no longer available through its original link, www.cityoffullerton.com/outbox. However, my reconstruction is consistent with information provided by the City in its declarations and the websites and information associated with this case.
II. QUALIFICATIONS AND BACKGROUND
6. I am President of Bambenek Consulting, LTD, a cybersecurity investigation and intelligence firm in Champaign, Illinois. I have worked 20 years in cybersecurity and consult with a wide range of law enforcement entities both in the United States and abroad on matters related to cybercrime or hostile nation-state activity. A true and correct copy of my curriculum vitae is attached as Exhibit A, and is incorporated by reference herein as if set forth in full.
7. I have been an adjunct lecturer in the Department of Computer Science and the School of Information Sciences at the University of Illinois teaching courses on digital forensics and cybersecurity. I am additionally an instructor at Parkland College also teaching a course on networking.
8. I am a co-author and helped design a digital forensics curriculum with the Information Trust Institute at the University of Illinois that lead to the create of interdisciplinary CS and Law courses on digital forensics and investigation.
9. Additionally, I have advised and continue to advise individuals on privacy and how to protect their information and privacy against hostile governments, abusive ex-partners, and variety of threat groups that target typically disadvantaged individuals and groups. I recently spoke at a conference discussing mobile malware attacks attributed to the Chinese government against Uighur Muslims and Tibetans .
10. I have assisted in law enforcement investigations including cases involving the 2016 presidential election including activity that helped retrieve some documents stolen by the Russian Government from the Democratic Congressional Campaign Committee. Most recently, I was the expert witness in Obeidallah v. Anglin, 2:17-CS-00720 (S. D. Ohio) where I testified in matters related to cryptocurrency and financial assets in a civil litigation matter.
11. I additionally provide auditing and consulting for a variety of companies, including law firms, on data protection and obligations around data security to comply with regulation or privilege.
12. I speak at conferences all over the world on matters relating to cybercrime investigation and threat intelligence and how to attribute malicious activity to individuals using technical information and metadata.
III. ANALYSIS
A. The City’s Declarations Provide No Evidence of “Hacking” or Unauthorized Access.
13. Dropbox is a web-based, file sharing application that allows individuals or organizations to store documents for their own use, share them with specific e-mail addresses (accounts are tied to e-mail address in Dropbox), or to make them available globally, worldwide, and without any access control.
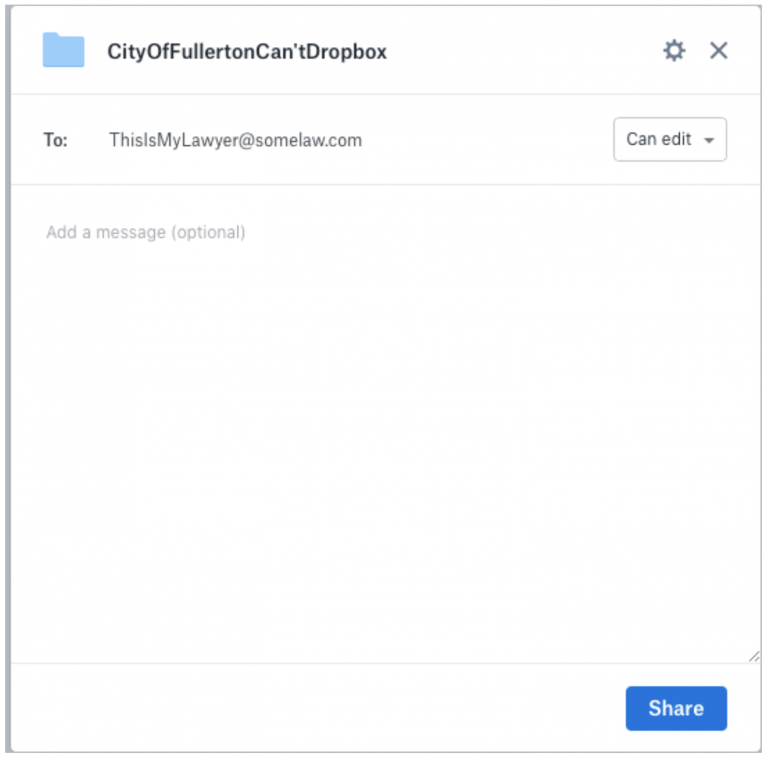
14. These settings are under the complete control of the owner of the files. In the web interface, there is a “share” button that allows file owners to either share their files or keep them confidential however they may see fit. For example, if a user wishes to share a file, via Dropbox, with their attorney for review, the user could send an email from the web interface to the attorney’s specific email address. Below is an example of a screenshot of the interface demonstrating this capability, which was created in a simulated folder created for this declaration:
15. Dropbox provides a variety of security settings and access limitations, which could expire a link at a given time, prevent downloads, and determine who has access. A screenshot of the possible access restrictions for the fictional folder used as an example in paragraph 9, is below:

16. It appears from the City’s declarations that the City set its folder permissions to intentionally allow anyone with the link can view it. When you select this level of access, Dropbox makes clear that “Anyone with this link can view the folder.” A screenshot of how this would appear to the creator of the folder or the administrator of the account appears below:
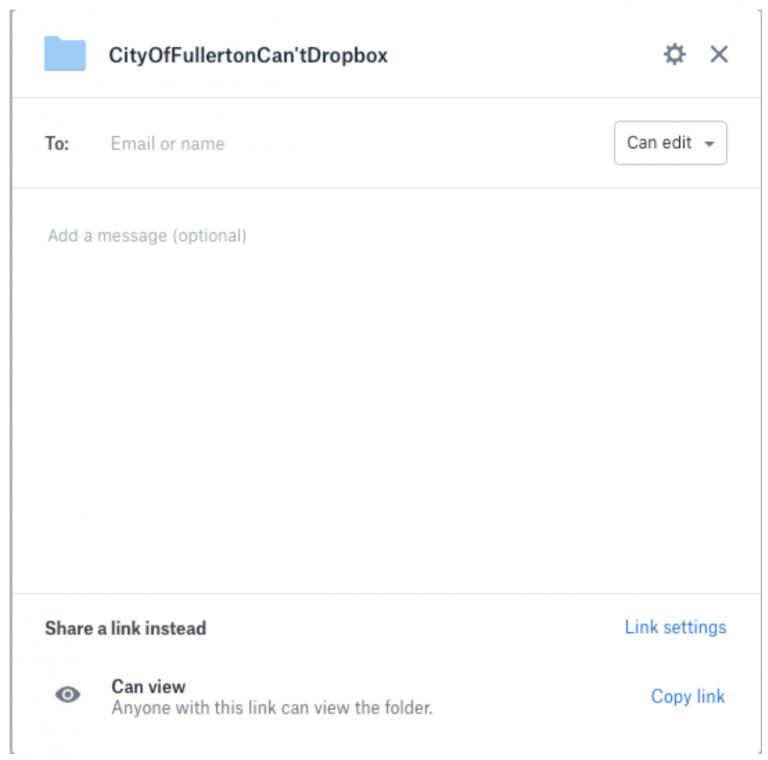
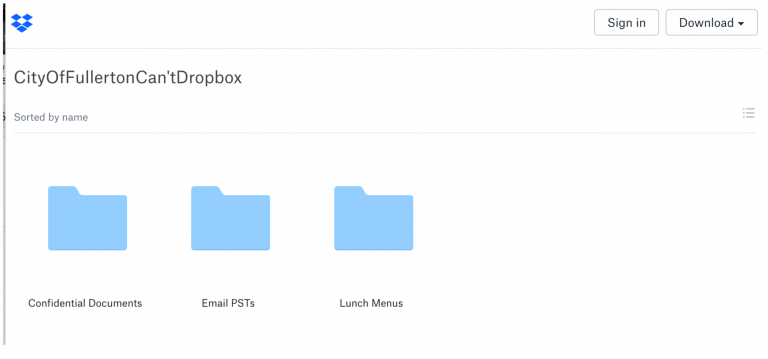
17. This means that the City created the URL (or internet address for the Dropbox account) and mere knowledge of that URL is sufficient for access. Anyone with knowledge of the URL would have access would only have to go to that website to find that the entire folder contents are available and visible, including any and all subfolders that are stored therein. An example of how that would appear to a user who enters the URL of an unrestricted Dropbox account appears below:
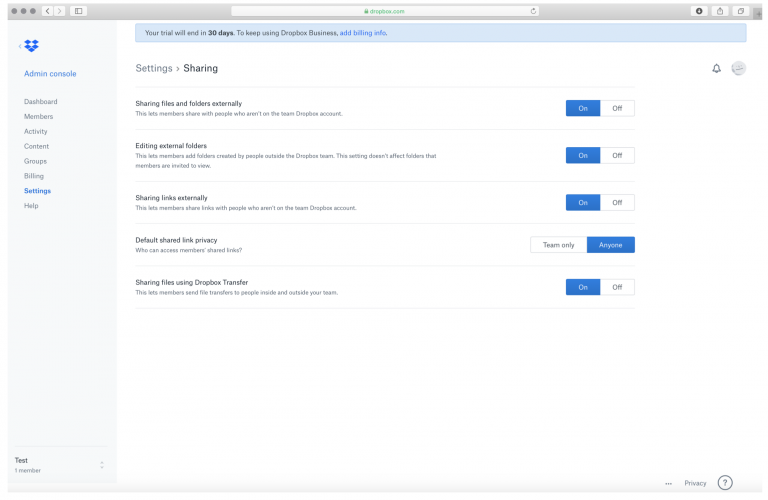
18. The City’s administrator for its Dropbox account could have also changed the global access restrictions so as to prevent information from being disclosed outside of various groups. An example of these global settings can be seen in this screenshot:
19. While explanations of the configuration of the City’s Dropbox security settings are notably absent from its declaration, there are no allegations in the City’s declarations that I have reviewed that even allege that there was any access or password restrictions on the City’s Dropbox account. This confirms that the set up I have described in the preceding paragraphs was the manner in which the City’s Dropbox account was configured and that anyone with knowledge of the URL could see and access the folders contained therein.
20. As the City set the configurations on its Dropbox account so anyone with the URL could access the folders, subfolders, (and by extension the content contained therein), they themselves made this information available to anyone, anywhere in the world to download at any time and for any reason.
21. Compounding these problems, the City then expressly changed its URL (or the address of its Dropbox) to www.cityoffullerton.com/outbox, making it appear that the Dropbox account was an ordinary part of the City’s website.
22. Accessing a typical Dropbox account would require someone to go to www.dropbox.com and enter their login credentials, including a user name/email address and a password. An example of this can be seen in the following screenshot:
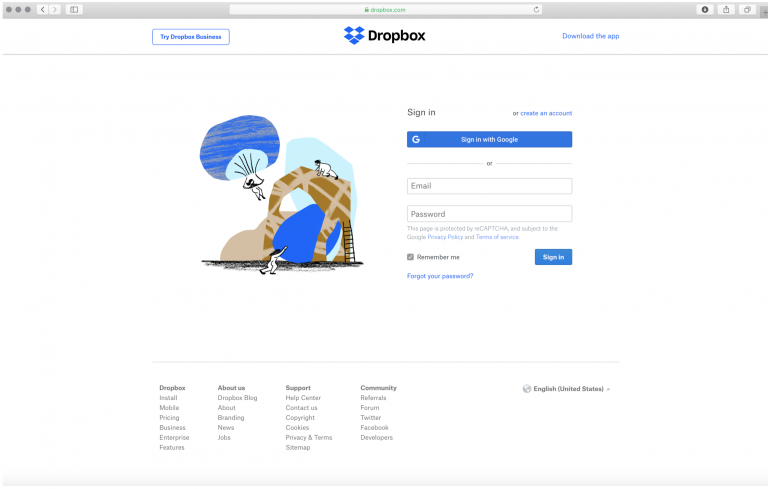
23. However, the City’s Dropbox was intentionally changed from this routine configuration, leaving no conspicuous way for the average user to know that the webpage housing the files was anything other than the City’s website.
24. From my review of the City’s website, the City also uses this configuration for various other types of disclosable public records and information. For example, information about the City’s meetings, including agenda and minutes, is available through the City’s website, by going to www.cityoffullerton.com, then clicking on the “Government” link, then on the “City Clerk” link, and then on the “Meetings and Agendas” link. However, this directs the user to the City’s Granicus account, which is a software platform used to manage government meeting data, including the storage and public access of agendas, minutes, and recordings of public meetings. The City uses OpenGov, another cloud-based software program, to manage and provide public access to its financial data. This is available directly through the City’s website by searching for “budget” in the website’s search feature, and clicking on the first link “City Budget”, and then clicking on link “OpenGov,” where the City directs users for information. There is no statement by the City in contained in any of these links or on any of these webpages which provide “express authorization” as to which links or files can be accessed by the public because the presumption is that information on a City website is public.
25. I have also reviewed the emails and communications described in and attached to the City’s declarations, but found no reference to any use restriction or admonishment until the City’s July 2019 correspondence to Kelly Aviles advising that accessing the Dropbox account was no longer authorized. Nor are there even any “terms of use” on the Plaintiff’s website to indicate such a restriction, even though that would not necessarily be sufficient to notify visitors that information on a public agency’s website was not intended for public access.
26. In my professional capacity as someone who evaluates security configurations of organizations with privileged and confidential information, I would have rated such a setup at an extremely high risk and priority for immediate change. The use of Dropbox to share confidential information or privileged communications is simply an unacceptable risk. Its use in this way can accurately be assessed as gross negligence.
27. This is particularly problematic for certain uses that are bound to keep information confidential. For example, attorneys have a duty of confidentiality, requiring them to take reasonable steps to maintain client information. (See California Rules of Professional Conduct, Rule 1.6; Cal. Bus. & Prof. Code § 6068.) This set up would be insufficient to ensure that confidential information is maintained. (See, e.g., https://www.americanbar.org/groups/business_law/publications/ blt/2017/09/01_kohut/; http://www.abajournal.com/magazine/article/ethics_secure_ client_communications/?utm_source=maestro&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=tech_monthly; https://www.calbar.ca.gov/Portals/0/documents/ethics/Opinions/2010-179-Interim-No-08-0002- PAW.pdf; https://www.sdcba.org/index.cfm?pg=Legal-Ethics-Opinion-2012-1.)
28. Similarly, Dropbox provides information on the appropriate use of its platform for HIPAA-related information, which requires specific configurations and access restrictions. It appears from Plaintiff’s declarations that the City failed to follow any of these steps to protect the information they stored on their Dropbox which they claim is confidential. In fact, the steps they did take removed what little security is typically available in a default configuration.
29. Typically, “hacking” refers to the use of some tool or technique that defeats defenses in a computer system. A password cracking program may try to guess the password for an account. A tool may attempt to exploit a vulnerability to get access to the underlying database of a website. Malware (or colloquially, a “computer virus”) may be installed on a victim machine to give access to information. There is no evidence that any tool, vulnerability, technique, or manipulation of a computer system occurred by the Defendants in this case, nor does the City allege that there was any such action.
30. In the terms of the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act and its related state statute, the specific formulation is “exceeding access” or “unauthorized access” of a protected computer system. In this case, the Defendant could not have exceeded or acquired unauthorized access. The computer system (Dropbox) gave Defendants and the public exactly the access that the City set in the first place.
That may have been a mistake on the City’s part, but the system worked exactly how it was designed with the exact settings it was given.
31. In light of the above and in the absence of other evidence not yet in the record, I conclude that the city had no technical restrictions on accessing the data so a computer system was not subverted to access the information. I further conclude there was no stated access restrictions, so no “administrative” access controls were subverted either.
B. VPN Use is Common and Appropriate
32. A VPN is an encryption-based technology to keep one’s network traffic secure.
33. The City and its “expert” appear to infer that its use demonstrates an ill intent or conscious of guilt. Use of a VPN says nothing about the propriety of the actions taken while using a VPN. There are a wide variety of use cases for this tool and like all tools, it can be used for good or for ill.
34. Journalists use VPNs. The Global Investigative Journalism Network recommends the use of VPNs for journalists . This is especially true for investigative journalists who are looking into government misconduct (like the kind uncovered and alleged by the journalist in this case). This is because governments often retaliate against those journalists and impose “personal costs” (such as losing one’s job) as a price for uncovering misconduct. Ironically, the City’s actions in retaliation for the reporting done by Defendants in this case is exactly the kind of case study for why this advice exists.
35. The FBI recommends that political campaigns use VPNs in light of election manipulation attempts, the Electronic Frontier Foundation produces a guide on personal VPNs designed for journalists, activists, LGBTQ persons, academic researchers, and others. A personal VPN might be used by a victim of a domestic abuses to make them harder to stalk.
36. A VPN is used often in business for secure access to corporate networks. A VPN can be used in academic to access University resources while remote. A VPN can be used to access video content, circumvent censorship, or to protect the confidentiality of someone who may be facing threats.
37. I, too, use several VPNs, one to access corporate files securely on untrusted networks, one to access campus resources provided for faculty and students only, and a personal VPN to watch “American” Netflix while overseas.
C. Attribution of VPN and Tor traffic is deeply flawed
38. There at no statements in Mr. Strebe’s declarations authenticating the logs attached as Exhibit A. The logs contain a table of information. The eighth column has no header but is populated with names from time to time (e.g. Tor, PureVPN, etc). There is no information about what this is, how it was gathered, or how it can be reproduced.
39. I created a Dropbox business account to compare the format of the logs that Dropbox itself generated. An example of what I saw in my experimental logs is below:
![]()
40. There appear to be key differences in the formats of the logs I obtained from the Dropbox account I created and the logs attached to Mr. Strebe’s declarations. For example, there is no corresponding column provided by Dropbox that maps to the 7th (“Region”) and 8th (untitled) columns in the logs attached as Exhibit A to Mr. Strebe’s original declaration. In Mr. Strebe’s supplemental declaration, the 8th untitled column is no longer included.
41. Also of note is that the logs I accessed from Dropbox using the account I created, unauthenticated users were logged, but only 1st and 2nd octet of the IP address were logged, the other half of the IP address was obscured (i.e. instead of seeing 12.24.36.48, what was produced shows 12.24.XXX.XXX).
42. While the City’s declarations do not state how the logs attached to Mr. Strebe’s declarations were generated, the discrepancies raise serious questions about the integrity and authentication of the logs attached to Mr. Strebe’s declarations, as they appear to have been manipulated or modified by the “expert,” compromising the integrity of the evidence.
43. Even presuming that these logs are authentic, and the information contained therein is accurate, there are serious flaws in the City’s analysis of what they purportedly show.
44. Several entries allege Mr. Ferguson’s account was logged into Dropbox and accessed city records purportedly from PureVPN (12/28/2017, 12/30/2017, and 3/29/2018 from Oslo and 10/26/2018, 10/27/2018, 10/30/2018, and 11/06/2018 from the Netherlands). There are no log entries produced by the City that indicate other occasions of Mr. Ferguson account accessing the City’s Dropbox. There are no logs at all indicating Mr. Curlee’s purported access.
45. Plaintiff then uses these brief occurrences to conclude that all access via PureVPN to Plaintiff’s Dropbox must be from Ferguson, Curlee, or their “unnamed associates.” (Strebe Dec., ¶ 40).
46. The City then reaches even farther to suggest all accesses via Tor must also be from the Defendants despite the complete and utter lack of evidence for that conclusion in their own exhibits. (See Strebe Dec., ¶ 60.)
47. The City and Mr. Strebe, undaunted by a complete lack of evidence and unhindered by any respect for appropriate investigative reasoning, then decide all access from foreign IPs otherwise unattributed must also be from the Defendants. (See Strebe Dec., ¶ 51.)
48. The only indication Plaintiff’s give for such reasoning is that some of the access attributed to Tor, PureVPN, or other “foreign” IP addresses was for documents responsive to records requests made by the Plaintiff that no one else would know. But this is a conclusion, not evidence. Nor is such a conclusion warranted based on the purported Dropbox logs.
49. PureVPN, according to Crunchbase has $15.7 million in revenue. Assuming that is correct, and based on the listed monthly cost of service (before discount) at $10.95/month , this would equate to approximately 120,000 PureVPN users. It defies credulity that Plaintiff could have eliminated all but 2 of those users from this activity.
50. According to the Tor Project, there are currently around 1.75 million active daily tor users . While there was at least some limited activity that Plaintiff could attribute to Defendant Ferguson via PureVPN, there is no activity over Tor that contains metadata implicating the Defendants.
51. The City and its “expert” stated there was a foreign access to Dropbox content on August 23, 2017. (See Strebe Dec., ¶ 37.) They argued this was “likely an authorized user” but provide absolutely no evidence for that conclusion. Who is the authorized user? How do they know its authorized? The ambiguity on that point stands in stark contrast to the certainty they express previously about all PureVPN, foreign VPN, and Tor traffic must be the Defendants.
52. Mr. Strebe also makes liberal use of printouts from a website myip.ms. This is not a forensically sound way to attribute IP addresses. There is no documentation as to how myip.ms works or where it gets its information, which makes it use questionable, at best.
IV. CONCLUSION
53. The evidence presented by the City in no way supports any allegation of “unauthorized access” or “exceeding access” of any computer system. The evidence shows that the City itself placed this information on the internet without access control allowing anyone full permission to download the content. The access logs, even if authenticated, do not substantiate, in the absence of other corroborating evidence, that all Tor, VPN, and foreign traffic belongs to the Defendants. Nor is Mr. Ferguson’s use of PureVPN a sufficient or even suggestive data point to implicate guilt.
I declare under penalty of perjury under the laws of the State of California that the foregoing is true and correct and that this declaration was executed on November 7, 2019, at Chula Vista, California.